Giacomini, K. M. & Sugiyama, Y. in Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Base of Therapeutics (eds Brunton, L. L., Lazo, J. S. & Parker, R. L.) 41–70 (McGraw-Hill, New York, 2006). This affiliate in a arbiter provides an accomplished overview of transporters.

Schinkel, A. H. & Jonker, J. W. Mammalian biologic address transporters of the ATP bounden cassette (ABC) family: an overview. Adv. Biologic Deliv. Rev. 55, 3–29 (2003). This arrangement provides an accomplished assay of ABC transporters that are important in biologic response.
Sai, Y. Biochemical and atomic pharmacological aspects of transporters as determinants of biologic disposition. Biologic Metab. Pharmacokinet. 20, 91–99 (2005).
Cascorbi, I. Role of pharmacogenetics of ATP-binding cassette transporters in the pharmacokinetics of drugs. Pharmacol. Ther. 112, 457–473 (2006).
Choudhuri, S. & Klaassen, C. D. Structure, function, expression, genomic organization, and distinct nucleotide polymorphisms of animal ABCB1 (MDR1), ABCC (MRP), and ABCG2 (BCRP) address transporters. Int. J. Toxicol. 25, 231–259 (2006).
Hediger, M. A. et al. The ABCs of solute carriers: physiological, dissection and ameliorative implications of animal film carriage proteins. Pflugers Arch. 447, 465–468 (2004).
Koepsell, H., Lips, K. & Volk, C. Polyspecific amoebic cation transporters: structure, function, physiological roles, and biopharmaceutical implications. Pharm. Res. 24, 1227–1251 (2007). This arrangement provides an accomplished assay of assorted transporters for amoebic cations (OCTs, OCTNs and MATEs).
Jonker, J. W., Wagenaar, E., Van Eijl, S. & Schinkel, A. H. Absence in the amoebic cation transporters 1 and 2 (Oct1/Oct2 [Slc22a1/Slc22a2]) in mice abolishes renal beard of amoebic cations. Mol. Corpuscle Biol. 23, 7902–7908 (2003).
Schinkel, A. H. et al. Multidrug attrition and the role of P-glycoprotein knockout mice. Eur. J. Blight 31A, 1295–1298 (1995).
Maeda, K. & Sugiyama, Y. Appulse of abiogenetic polymorphisms of transporters on the pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and toxicological backdrop of anionic drugs. Biologic Metab. Pharmacokinet. 23, 223–235 (2008).
Sissung, T. M., Gardner, E. R., Gao, R. & Figg, W. D. Pharmacogenetics of film transporters: a assay of accepted approaches. Methods Mol. Biol. 448, 41–62 (2008).
Huang, S. M., Temple, R., Throckmorton, D. C. & Lesko, L. J. Biologic alternation studies: abstraction design, abstracts analysis, and implications for dosing and labeling. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 81, 298–304 (2007).
Huang, S. M. et al. New era in biologic alternation evaluation: US Food and Biologic Administration amend on CYP enzymes, transporters, and the advice process. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 48, 662–670 (2008).
US Department of Bloom and Animal Services, Food and Biologic Administration, Center for Biologic Appraisal and Research (CDER), Center for Biologics Appraisal and Research (CBER). Advice for Industry. Biologic Alternation Studies — Abstraction Design, Abstracts Analysis, and Implications for Dosing and Labeling. US FDA website [online], (2006). This website provides accepted FDA guidances for DDI studies. For adapted guidances see the websites in Further information.
Zhang, L., Zhang, Y. D., Strong, J. M., Reynolds, K. S. & Huang, S. M. A authoritative angle on transporter-based biologic interactions. Xenobiotica 38, 709–724 (2008). This commodity provides an FDA angle about the role of transporters in DDIs.
Zhang, L., Strong, J. M., Qiu, W., Lesko, L. J. & Huang, S. M. Scientific perspectives on biologic transporters and their role in biologic interactionst. Mol. Pharm. 3, 62–69 (2006).
Raub, T. J. P-glycoprotein acceptance of substrates and abstention through rational biologic design. Mol. Pharm. 3, 3–25 (2006).
Miller, D. S., Bauer, B. & Hartz, A. M. Modulation of P-glycoprotein at the blood–brain barrier: opportunities to advance axial afraid arrangement pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 60, 196–209 (2008).
Kimura, Y., Morita, S. Y., Matsuo, M. & Ueda, K. Apparatus of multidrug acceptance by MDR1/ABCB1. Blight Sci. 98, 1303–1310 (2007).
Chinn, L. W. & Kroetz, D. L. ABCB1 pharmacogenetics: progress, pitfalls, and promise. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 81, 265–269 (2007).
Zhou, S. F. Structure, action and adjustment of P-glycoprotein and its analytic appliance in biologic disposition. Xenobiotica 38, 802–832 (2008).
Aller, S. G. et al. Anatomy of P-glycoprotein reveals a atomic base for poly-specific biologic binding. Science 323, 1718–1722 (2009). This arrangement describes the aboriginal atomic anatomy of abrasion P-gp.
Zhou, Y., Gottesman, M. M. & Pastan, I. Studies of animal MDR1–MDR2 chimeras authenticate the anatomic adequation of a above transmembrane articulation of the multidrug agent and phosphatidylcholine flippase. Mol. Corpuscle Biol. 19, 1450–1459 (1999).
Carrier, I., Julien, M. & Gros, P. Assay of catalytic carboxylate mutants E552Q and E1197Q suggests agee ATP hydrolysis by the two nucleotide-binding domains of P-glycoprotein. Biochemistry 42, 12875–12885 (2003).
Loo, T. W., Bartlett, M. C. & Clarke, D. M. Val133 and Cys137 in transmembrane articulation 2 are abutting to Arg935 and Gly939 in transmembrane articulation 11 of animal P-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 18232–18238 (2004).
Feng, B. et al. In vitro P-glycoprotein assays to adumbrate the in vivo interactions of P-glycoprotein with drugs in the axial afraid system. Biologic Metab. Dispos. 36, 268–275 (2008).
Yamazaki, M. et al. In vitro substrate identification studies for P-glycoprotein-mediated transport: breed aberration and adequation of in vivo results. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 296, 723–735 (2001).
Sasongko, L. et al. Imaging P-glycoprotein carriage action at the animal blood–brain barrier with positron discharge tomography. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 77, 503–514 (2005).
Kurnik, D. et al. Tariquidar, a careful P-glycoprotein inhibitor, does not potentiate loperamide’s opioid academician furnishings in bodies admitting abounding inhibition of lymphocyte P-glycoprotein. Anesthesiology 109, 1092–1099 (2008).
Sadeque, A. J., Wandel, C., He, H., Shah, S. & Wood, A. J. Added biologic commitment to the academician by P-glycoprotein inhibition. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 68, 231–237 (2000).
Eyal, S., Hsiao, P. & Unadkat, J. D. Biologic interactions at the blood–brain barrier: actuality or fantasy? Pharmacol. Ther. 123, 80–104 (2009).
Williams, J. A. et al. PhRMA white cardboard on ADME pharmacogenomics. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 48, 849–889 (2008).
Wakabayashi, K., Tamura, A., Saito, H., Onishi, Y. & Ishikawa, T. Animal ABC agent ABCG2 in xenobiotic aegis and redox biology. Biologic Metab. Rev. 38, 371–391 (2006).
Robey, R. W. et al. ABCG2: a perspective. Adv. Biologic Deliv. Rev. 61, 3–13 (2009).
Doyle, L. A. et al. A multidrug attrition agent from animal MCF-7 breast blight cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 15665–15670 (1998).
van Herwaarden, A. E. & Schinkel, A. H. The action of breast blight attrition protein in epithelial barriers, axis beef and milk beard of drugs and xenotoxins. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 27, 10–16 (2006).
Vlaming, M. L., Lagas, J. S. & Schinkel, A. H. Physiological and pharmacological roles of ABCG2 (BCRP): contempo allegation in Abcg2 knockout mice. Adv. Biologic Deliv. Rev. 61, 14–25 (2009).
Matsson, P. et al. A all-around biologic inhibition arrangement for the animal ATP-binding cassette agent breast blight attrition protein (ABCG2). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 323, 19–30 (2007).
Nicolle, E. et al. QSAR assay and atomic clay of ABCG2-specific inhibitors. Adv. Biologic Deliv. Rev. 61, 34–46 (2009).
Saito, H. et al. A new action of accelerated screening and quantitative structure–activity accord assay to appraise animal ATP-binding cassette agent ABCG2-drug interactions. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 317, 1114–1124 (2006).
Hirano, M. et al. Captivation of BCRP (ABCG2) in the biliary abolishment of pitavastatin. Mol. Pharmacol. 68, 800–807 (2005).
Enokizono, J., Kusuhara, H. & Sugiyama, Y. Aftereffect of breast blight attrition protein (Bcrp/Abcg2) on the disposition of phytoestrogens. Mol. Pharmacol. 72, 967–975 (2007).
Hegedus, C. et al. Ins and outs of the ABCG2 multidrug transporter: an amend on in vitro anatomic assays. Adv. Biologic Deliv. Rev. 61, 47–56 (2009).
de Vries, N. A. et al. P-glycoprotein and breast blight attrition protein: two ascendant transporters alive calm in attached the academician assimilation of topotecan. Clin. Blight Res. 13, 6440–6449 (2007).
Zaher, H. et al. Breast blight attrition protein (Bcrp/abcg2) is a above account of sulfasalazine assimilation and abolishment in the mouse. Mol. Pharm. 3, 55–61 (2006).
Merino, G., Jonker, J. W., Wagenaar, E., van Herwaarden, A. E. & Schinkel, A. H. The breast blight attrition protein (BCRP/ABCG2) affects pharmacokinetics, hepatobiliary excretion, and milk beard of the antibacterial nitrofurantoin. Mol. Pharmacol. 67, 1758–1764 (2005).
Merino, G. et al. Breast blight attrition protein (BCRP/ABCG2) transports fluoroquinolone antibiotics and affects their articulate availability, pharmacokinetics, and milk secretion. Biologic Metab. Dispos. 34, 690–695 (2006).
Oostendorp, R. L., Buckle, T., Beijnen, J. H., van Tellingen, O. & Schellens, J. H. The aftereffect of P-gp (Mdr1a/1b), BCRP (Bcrp1) and P-gp/BCRP inhibitors on the in vivo absorption, distribution, metabolism and abolishment of imatinib. Invest. New Drugs 27, 31–40 (2009).
Yamasaki, Y. et al. Pharmacogenetic assuming of sulfasalazine disposition based on NAT2 and ABCG2 (BCRP) gene polymorphisms in humans. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 84, 95–103 (2008).
Cusatis, G. & Sparreboom, A. Pharmacogenomic accent of ABCG2. Pharmacogenomics 9, 1005–1009 (2008).
Cusatis, G. et al. Pharmacogenetics of ABCG2 and adverse reactions to gefitinib. J. Natl Blight Inst. 98, 1739–1742 (2006).
Polgar, O., Robey, R. W. & Bates, S. E. ABCG2: structure, action and role in biologic response. Expert Opin. Biologic Metab. Toxicol. 4, 1–15 (2008).
Keskitalo, J. E. et al. ABCG2 polymorphism clearly affects the pharmacokinetics of atorvastatin and rosuvastatin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 86, 197–203 (2009).
Zhang, W. et al. Role of BCRP 421C>A polymorphism on rosuvastatin pharmacokinetics in advantageous Chinese males. Clin. Chim. Acta 373, 99–103 (2006).
Morisaki, K. et al. Distinct nucleotide polymorphisms adapt the agent action of ABCG2. Blight Chemother. Pharmacol. 56, 161–172 (2005).
Aoki, M. et al. Kidney-specific announcement of animal amoebic cation agent 2 (OCT2/SLC22A2) is adapted by DNA methylation. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 295, F165–F170 (2008).

Koepsell, H. & Endou, H. The SLC22 biologic agent family. Pflugers Arch. 447, 666–676 (2004).
Wright, S. H. Role of amoebic cation transporters in the renal administration of ameliorative agents and xenobiotics. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 204, 309–319 (2005).
Urban, T. J. & Giacomini, K. M. in Biologic Transporters (eds You, G. & Morris, M. E.) 11–33 (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2007).
Ciarimboli, G. Amoebic cation transporters. Xenobiotica 38, 936–971 (2008).
Nigam, S. K., Bush, K. T. & Bhatnagar, V. Biologic and adulteration administration by the OAT amoebic anion transporters in the branch and added tissues. Nature Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 3, 443–448 (2007). This arrangement provides an accomplished assay of OATs.
Rizwan, A. N. & Burckhardt, G. Amoebic anion transporters of the SLC22 family: biopharmaceutical, physiological, and dissection roles. Pharm. Res. 24, 450–470 (2007).
Srimaroeng, C., Perry, J. L. & Pritchard, J. B. Physiology, structure, and adjustment of the cloned amoebic anion transporters. Xenobiotica 38, 889–935 (2008).
Ahlin, G. et al. Structural requirements for biologic inhibition of the alarmist specific animal amoebic cation carriage protein 1. J. Med. Chem. 51, 5932–5942 (2008).
Okura, T., Ito, R., Ishiguro, N., Tamai, I. & Deguchi, Y. Blood–brain barrier carriage of pramipexole, a dopamine D2 agonist. Life Sci. 80, 1564–1571 (2007).
Glube, N. & Langguth, P. Caki-1 beef as a archetypal arrangement for the alternation of renally buried drugs with OCT3. Nephron Physiol. 108, 18–28 (2008).
Glube, N., Giessl, A., Wolfrum, U. & Langguth, P. Caki-1 beef represent an in vitro archetypal arrangement for belief the animal adjacent tubule epithelium. Nephron Exp. Nephrol. 107, e47–e56 (2007).
Muller, J. et al. Biologic specificity and abdominal film localization of animal amoebic cation transporters (OCT). Biochem. Pharmacol. 70, 1851–1860 (2005).
Rytting, E., Bryan, J., Southard, M. & Audus, K. L. Low-affinity uptake of the beaming amoebic cation 4-(4-(dimethylamino)styryl)-N-methylpyridinium iodide (4-Di-1-ASP) in BeWo cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 73, 891–900 (2007).
Kaler, G. et al. Structural aberration governs substrate specificity for amoebic anion agent (OAT) homologs. Abeyant alien assay by OAT ancestors members. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 23841–23853 (2007).
Truong, D. M., Kaler, G., Khandelwal, A., Swaan, P. W. & Nigam, S. K. Multi-level assay of amoebic anion transporters 1, 3, and 6 reveals above differences in structural determinants of antiviral discrimination. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 8654–8663 (2008).
Jonker, J. W. et al. Bargain hepatic uptake and abdominal abolishment of amoebic cations in mice with a targeted disruption of the amoebic cation agent 1 (Oct1 [Slc22a1]) gene. Mol. Corpuscle Biol. 21, 5471–5477 (2001).
Shu, Y. et al. Aftereffect of abiogenetic aberration in the amoebic cation agent 1 (OCT1) on metformin action. J. Clin. Invest. 117, 1422–1431 (2007).
Wang, D. S. et al. Captivation of amoebic cation agent 1 in hepatic and abdominal administration of metformin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 302, 510–515 (2002).
Eraly, S. A. et al. Decreased renal amoebic anion beard and claret accession of autogenous amoebic anions in OAT1 knock-out mice. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 5072–5083 (2006).
Vallon, V. et al. Overlapping in vitro and in vivo specificities of the amoebic anion transporters OAT1 and OAT3 for bend and thiazide diuretics. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 294, F867–F873 (2008).
Shu, Y. et al. Aftereffect of abiogenetic aberration in the amoebic cation agent 1, OCT1, on metformin pharmacokinetics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 83, 273–280 (2008).
Zhou, K. et al. Reduced-function SLC22A1 polymorphisms encoding amoebic cation agent 1 and glycemic acknowledgment to metformin: a GoDARTS study. Diabetes 58, 1434–1439 (2009).
White, D. L. et al. OCT-1-mediated arrival is a key account of the intracellular uptake of imatinib but not nilotinib (AMN107): bargain OCT-1 action is the account of low in vitro acuteness to imatinib. Claret 108, 697–704 (2006).
White, D. L. et al. Most CML patients who accept a suboptimal acknowledgment to imatinib accept low OCT-1 activity: college doses of imatinib may affected the abrogating appulse of low OCT-1 activity. Claret 110, 4064–4072 (2007).
Wang, Z. J., Yin, O. Q., Tomlinson, B. & Chow, M. S. OCT2 polymorphisms and in-vivo renal anatomic consequence: studies with metformin and cimetidine. Pharmacogenet. Genomics 18, 637–645 (2008).
Song, I. S. et al. Abiogenetic variants of the amoebic cation agent 2 access the disposition of metformin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 84, 559–562 (2008).
Chen, Y. et al. Aftereffect of abiogenetic aberration in the amoebic cation agent 2 on the renal abolishment of metformin. Pharmacogenet. Genomics 19, 497–504 (2009).
Tirona, R. G. & Kim, R. B. in Biologic Transporters (eds You, G. & Morris, M. E.) 75–104 (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2007).
Hagenbuch, B. & Gui, C. Xenobiotic transporters of the animal amoebic anion alteration polypeptides (OATP) family. Xenobiotica 38, 778–801 (2008). This arrangement provides an accomplished assay of OATPs.
Leuthold, S. et al. Mechanisms of pH-gradient apprenticed carriage advised by amoebic anion polypeptide transporters. Am. J. Physiol. Corpuscle Physiol. 296, C570–C582 (2009).
Hagenbuch, B. & Meier, P. J. The superfamily of amoebic anion alteration polypeptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1609, 1–18 (2003).
Tirona, R. G., Leake, B. F., Merino, G. & Kim, R. B. Polymorphisms in OATP-C: identification of assorted allelic variants associated with adapted carriage action amid European- and African-Americans. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 35669–35675 (2001).
Hsiang, B. et al. A atypical animal hepatic amoebic anion alteration polypeptide (OATP2). Identification of a liver-specific animal amoebic anion alteration polypeptide and identification of rat and animal hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitor transporters. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 37161–37168 (1999).
Konig, J., Cui, Y., Nies, A. T. & Keppler, D. A atypical animal amoebic anion alteration polypeptide localized to the basolateral hepatocyte membrane. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Alarmist Physiol. 278, G156–G164 (2000).
Abe, T. et al. Identification of a atypical gene ancestors encoding animal liver-specific amoebic anion agent LST-1. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 17159–17163 (1999).
Kullak-Ublick, G. A. et al. Amoebic anion-transporting polypeptide B (OATP-B) and its anatomic allegory with three added OATPs of animal liver. Gastroenterology 120, 525–533 (2001).
Gui, C. & Hagenbuch, B. Amino acerbic residues in transmembrane area 10 of amoebic anion alteration polypeptide 1B3 are analytical for cholecystokinin octapeptide transport. Biochemistry 47, 9090–9097 (2008).
Ismair, M. G. et al. Hepatic uptake of cholecystokinin octapeptide by amoebic anion-transporting polypeptides OATP4 and OATP8 of rat and animal liver. Gastroenterology 121, 1185–1190 (2001).
Shitara, Y., Sato, H. & Sugiyama, Y. Appraisal of drug–drug alternation in the hepatobiliary and renal carriage of drugs. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 45, 689–723 (2005).
Letschert, K., Komatsu, M., Hummel-Eisenbeiss, J. & Keppler, D. Vectorial carriage of the peptide CCK-8 by double-transfected MDCKII beef durably cogent the amoebic anion agent OATP1B3 (OATP8) and the consign pump ABCC2. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 313, 549–556 (2005).
Matsushima, S. et al. Identification of the hepatic address transporters of amoebic anions appliance double-transfected Madin-Darby basset branch II beef cogent animal amoebic anion-transporting polypeptide 1B1 (OATP1B1)/multidrug resistance-associated protein 2, OATP1B1/multidrug attrition 1, and OATP1B1/breast blight attrition protein. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 314, 1059–1067 (2005).
Ishiguro, N. et al. Predominant addition of OATP1B3 to the hepatic uptake of telmisartan, an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, in humans. Biologic Metab. Dispos. 34, 1109–1115 (2006).
Noe, J., Portmann, R., Brun, M. E. & Funk, C. Substrate-dependent drug–drug interactions amid gemfibrozil, fluvastatin and added amoebic anion-transporting peptide (OATP) substrates on OATP1B1, OATP2B1, and OATP1B3. Biologic Metab. Dispos. 35, 1308–1314 (2007).
Zaher, H. et al. Targeted disruption of murine amoebic anion-transporting polypeptide 1b2 (Oatp1b2/Slco1b2) decidedly alters disposition of prototypal biologic substrates pravastatin and rifampin. Mol. Pharmacol. 74, 320–329 (2008).
Lu, H. et al. Assuming of amoebic anion alteration polypeptide 1b2-null mice: capital role in hepatic uptake/toxicity of phalloidin and microcystin-LR. Toxicol. Sci. 103, 35–45 (2008).
Neuvonen, P. J., Niemi, M. & Backman, J. T. Biologic interactions with lipid-lowering drugs: mechanisms and analytic relevance. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 80, 565–581 (2006).
Shitara, Y., Itoh, T., Sato, H., Li, A. P. & Sugiyama, Y. Inhibition of transporter-mediated hepatic uptake as a apparatus for drug–drug alternation amid cerivastatin and cyclosporin A. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 304, 610–616 (2003).
Pasanen, M. K., Neuvonen, P. J. & Niemi, M. All-around assay of abiogenetic aberration in SLCO1B1. Pharmacogenomics 9, 19–33 (2008).
Mwinyi, J., Johne, A., Bauer, S., Roots, I. & Gerloff, T. Evidence for changed furnishings of OATP-C (SLC21A6) 5 and 1b haplotypes on pravastatin kinetics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 75, 415–421 (2004).
Nishizato, Y. et al. Polymorphisms of OATP-C (SLC21A6) and OAT3 (SLC22A8) genes: after-effects for pravastatin pharmacokinetics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 73, 554–565 (2003).
Chung, J. Y. et al. Aftereffect of OATP1B1 (SLCO1B1) alternative alleles on the pharmacokinetics of pitavastatin in advantageous volunteers. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 78, 342–350 (2005).
Pasanen, M. K., Neuvonen, M., Neuvonen, P. J. & Niemi, M. SLCO1B1 polymorphism clearly affects the pharmacokinetics of simvastatin acid. Pharmacogenet. Genomics 16, 873–879 (2006).
Pasanen, M. K., Fredrikson, H., Neuvonen, P. J. & Niemi, M. Adapted furnishings of SLCO1B1 polymorphism on the pharmacokinetics of atorvastatin and rosuvastatin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 82, 726–733 (2007).
Lee, E. et al. Rosuvastatin pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenetics in white and Asian capacity residing in the aforementioned environment. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 78, 330–341 (2005).
Niemi, M. et al. Polymorphic amoebic anion alteration polypeptide 1B1 is a above account of repaglinide pharmacokinetics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 77, 468–478 (2005).

Katz, D. A. et al. Amoebic anion alteration polypeptide 1B1 action classified by SLCO1B1 genotype influences atrasentan pharmacokinetics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 79, 186–196 (2006).
Xiang, X. et al. Pharmacogenetics of SLCO1B1 gene and the appulse of *1b and *15 haplotypes on irinotecan disposition in Asian blight patients. Pharmacogenet. Genomics 16, 683–691 (2006).
Oswald, S., Scheuch, E., Cascorbi, I. & Siegmund, W. A LC-MS/MS adjustment to quantify the atypical cholesterol blurred biologic ezetimibe in animal serum, urine and carrion in advantageous capacity genotyped for SLCO1B1. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 830, 143–150 (2006).
Link, E. et al. SLCO1B1 variants and statin-induced myopathy — a genomewide study. N. Engl. J. Med. 359, 789–799 (2008). This arrangement represents the aboriginal genome-wide affiliation abstraction in the pharmacogenomics of, and highlights the important role of, biologic transporters in biologic safety.
Uchida, Y., Kamiie, J., Ohtsuki, S. & Terasaki, T. Multichannel aqueous chromatography-tandem accumulation spectrometry cocktail adjustment for absolute substrate assuming of multidrug resistance-associated protein 4 transporter. Pharm. Res. 24, 2281–2296 (2007).
Ishikawa, T. et al. Accelerated screening of animal ATP-binding cassette agent action and abiogenetic polymorphisms: new strategies in pharmacogenomics. Methods Enzymol. 400, 485–510 (2005).
Keppler, D., Jedlitschky, G. & Leier, I. Carriage action and substrate specificity of multidrug attrition protein. Methods Enzymol. 292, 607–616 (1998).
Hilgendorf, C. et al. Announcement of thirty-six biologic agent genes in animal intestine, liver, kidney, and organotypic corpuscle lines. Biologic Metab. Dispos. 35, 1333–1340 (2007).
Sauvant, C. et al. Action of EGF and PGE2 on basolateral amoebic anion uptake in aerial adjacent renal tubules and hOAT1 bidding in animal branch epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 286, F774–F783 (2004).
Lee, S. H. & Sinko, P. J. siRNA — accepting the bulletin out. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 27, 401–410 (2006).
Yue, W., Abe, K. & Brouwer, K. L. Knocking bottomward breast blight attrition protein (Bcrp) by adenoviral vector-mediated RNA arrest (RNAi) in sandwich-cultured rat hepatocytes: a atypical apparatus to appraise the addition of Bcrp to biologic biliary excretion. Mol. Pharm. 6, 134–143 (2009).
Zhang, W. et al. Silencing the breast blight attrition protein announcement and action in caco-2 beef appliance lentiviral vector-based abbreviate ambit RNA. Biologic Metab. Dispos. 37, 737–744 (2009).
Keppler, D. Uptake and address transporters for conjugates in animal hepatocytes. Methods Enzymol. 400, 531–542 (2005).
Sasaki, M. et al. Anticipation of in vivo biliary approval from the in vitro transcellular carriage of amoebic anions beyond a double-transfected Madin-Darby basset branch II monolayer cogent both rat amoebic anion alteration polypeptide 4 and multidrug attrition associated protein 2. Mol. Pharmacol. 66, 450–459 (2004).
Sasaki, M., Suzuki, H., Ito, K., Abe, T. & Sugiyama, Y. Transcellular carriage of amoebic anions beyond a double-transfected Madin-Darby basset branch II corpuscle monolayer cogent both animal amoebic anion-transporting polypeptide (OATP2/SLC21A6) and multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2/ABCC2). J. Biol. Chem. 277, 6497–6503 (2002).
Cui, Y., Konig, J. & Keppler, D. Vectorial carriage by double-transfected beef cogent the animal uptake agent SLC21A8 and the aciculate consign pump ABCC2. Mol. Pharmacol. 60, 934–943 (2001).
Bartholome, K. et al. Data-based algebraic clay of vectorial carriage beyond double-transfected polarized cells. Biologic Metab. Dispos. 35, 1476–1481 (2007).
Marion, T. L., Leslie, E. M. & Brouwer, K. L. Use of sandwich-cultured hepatocytes to appraise broken acerbity acerbic carriage as a apparatus of drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Mol. Pharm. 4, 911–918 (2007).
Liu, X. et al. Biliary abolishment in primary rat hepatocytes able in a collagen-sandwich configuration. Am. J. Physiol. 277, G12–G21 (1999).
LeCluyse, E. L., Audus, K. L. & Hochman, J. H. Formation of all-encompassing canalicular networks by rat hepatocytes able in collagen-sandwich configuration. Am. J. Physiol. 266, C1764–C1774 (1994).
Hoffmaster, K. A. et al. P-glycoprotein expression, localization, and action in sandwich-cultured primary rat and animal hepatocytes: appliance to the hepatobiliary disposition of a archetypal opioid peptide. Pharm. Res. 21, 1294–1302 (2004).
Abe, K., Bridges, A. S. & Brouwer, K. L. Use of sandwich-cultured animal hepatocytes to adumbrate biliary approval of angiotensin II receptor blockers and HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Biologic Metab. Dispos. 37, 447–452 (2009).
Klaassen, C. D. & Lu, H. Xenobiotic transporters: ascribing action from gene knockout and alteration studies. Toxicol. Sci. 101, 186–196 (2008).
Schinkel, A. H. et al. Disruption of the abrasion Mdr1a P-glycoprotein gene leads to a absence in the blood–brain barrier and to added acuteness to drugs. Corpuscle 77, 491–502 (1994). This arrangement was the aboriginal abstraction that approved the important role of P-gp in the blood–brain barrier in the abrasion and its role in free biologic sensitivity.
Polli, J. W. et al. An abrupt agitator role of P-glycoprotein and breast blight attrition protein on the axial afraid arrangement assimilation of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor lapatinib (N-{3-chloro-4-[(3-fluorobenzyl)oxy]phenyl}-6-[5-({[2-(methylsulfonyl)ethy l]amino}methyl)-2-furyl]-4-quinazolinamine; GW572016). Biologic Metab. Dispos. 37, 439–442 (2009).
Zamek-Gliszczynski, M. J., Kalvass, J. C., Pollack, G. M. & Brouwer, K. L. Accord amid drug/metabolite acknowledgment and crime of excretory carriage function. Biologic Metab. Dispos. 37, 386–390 (2009).
Li, M. et al. Identification of interspecies aberration in address transporters of hepatocytes from dog, rat, monkey and human. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 35, 114–126 (2008).
Takekuma, Y. et al. Aberration amid pharmacokinetics of mycophenolic acerbic (MPA) in rats and that in bodies is acquired by adapted affinities of MRP2 to a glucuronized form. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 10, 71–85 (2007).
Zamek-Gliszczynski, M. J. et al. Cogwheel captivation of Mrp2 (Abcc2) and Bcrp (Abcg2) in biliary abolishment of 4-methylumbelliferyl glucuronide and sulfate in the rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 319, 459–467 (2006).
Zamek-Gliszczynski, M. J. et al. The important role of Bcrp (Abcg2) in the biliary abolishment of sulfate and glucuronide metabolites of acetaminophen, 4-methylumbelliferone, and harmol in mice. Mol. Pharmacol. 70, 2127–2133 (2006).
Merino, G., van Herwaarden, A. E., Wagenaar, E., Jonker, J. W. & Schinkel, A. H. Sex-dependent announcement and action of the ATP-binding cassette agent breast blight attrition protein (BCRP/ABCG2) in liver. Mol. Pharmacol. 67, 1765–1771 (2005).
Vlaming, M. L. et al. Carcinogen and anticancer biologic carriage by Mrp2 in vivo: studies appliance Mrp2 (Abcc2) knockout mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 318, 319–327 (2006).
Chu, X. Y. et al. Assuming of mice defective the multidrug attrition protein MRP2 (ABCC2). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 317, 579–589 (2006).
van de Steeg, E. et al. Methotrexate pharmacokinetics in transgenic mice with liver-specific announcement of animal amoebic anion-transporting polypeptide 1B1 (SLCO1B1). Biologic Metab. Dispos. 37, 277–281 (2009).
Hirano, M., Maeda, K., Shitara, Y. & Sugiyama, Y. Drug–drug alternation amid pitavastatin and assorted drugs via OATP1B1. Biologic Metab. Dispos. 34, 1229–1236 (2006).
Maeda, K. & Sugiyama, Y. in Biologic Transporters (eds You, G. & Morris, M. E.) 557–588 (John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New York, 2007).
Hirano, M., Maeda, K., Shitara, Y. & Sugiyama, Y. Addition of OATP2 (OATP1B1) and OATP8 (OATP1B3) to the hepatic uptake of pitavastatin in humans. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 311, 139–146 (2004).
Watanabe, T., Kusuhara, H., Maeda, K., Shitara, Y. & Sugiyama, Y. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic clay to adumbrate transporter-mediated approval and administration of pravastatin in humans. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 328, 652–662 (2009).
Paine, S. W., Parker, A. J., Gardiner, P., Webborn, P. J. & Riley, R. J. Anticipation of the pharmacokinetics of atorvastatin, cerivastatin, and indomethacin appliance active models activated to abandoned rat hepatocytes. Biologic Metab. Dispos. 36, 1365–1374 (2008).
Poirier, A., Funk, C., Scherrmann, J. M. & Lave, T. Mechanistic clay of hepatic carriage from beef to accomplished body: appliance to napsagatran and fexofenadine. Mol. Pharm. 6, 1716–1733 (2009).
Takano, A. et al. Appraisal of in vivo P-glycoprotein action at the blood–brain barrier amid MDR1 gene polymorphisms by appliance 11C-verapamil. J. Nucl. Med. 47, 1427–1433 (2006).
Guhlmann, A. et al. Noninvasive appraisal of hepatobiliary and renal abolishment of cysteinyl leukotrienes by positron discharge tomography. Hepatology 21, 1568–1575 (1995).
de Vries, E. F. et al. Can celecoxib affect P-glycoprotein-mediated biologic efflux? A microPET study. Nucl. Med. Biol. 35, 459–466 (2008).
Piwnica-Worms, D. et al. Anatomic imaging of multidrug-resistant P-glycoprotein with an organotechnetium complex. Blight Res. 53, 977–984 (1993).
Hendrikse, N. H. et al. In vivo imaging of hepatobiliary carriage action advised by multidrug attrition associated protein and P-glycoprotein. Blight Chemother. Pharmacol. 54, 131–138 (2004).
Cebecauerova, D. et al. Dual ancestral jaundice: accompanying accident of mutations causing Gilbert’s and Dubin–Johnson syndrome. Gastroenterology 129, 315–320 (2005).
Bujanover, Y., Bar-Meir, S., Hayman, I. & Baron, J. 99mTc-HIDA cholescintigraphy in accouchement with Dubin–Johnson syndrome. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2, 311–312 (1983).
Ghibellini, G., Leslie, E. M., Pollack, G. M. & Brouwer, K. L. Use of Tc-99m mebrofenin as a analytic delving to appraise adapted hepatobiliary transport: affiliation of in vitro, pharmacokinetic modeling, and simulation studies. Pharm. Res. 25, 1851–1860 (2008).
Ghibellini, G. et al. In vitro–in vivo alternation of hepatobiliary biologic approval in humans. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 81, 406–413 (2007).
Ghibellini, G., Johnson, B. M., Kowalsky, R. J., Heizer, W. D. & Brouwer, K. L. A atypical adjustment for the assurance of biliary approval in humans. AAPS J. 6, e33 (2004).
Michael, M. et al. Accord of hepatic anatomic imaging to irinotecan pharmacokinetics and abiogenetic ambit of biologic elimination. J. Clin. Oncol. 24, 4228–4235 (2006).
Wong, M. et al. Predictors of vinorelbine pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in patients with cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 24, 2448–2455 (2006).
Zhang, Y. & Benet, L. Z. The gut as a barrier to biologic absorption: accumulated role of cytochrome P450 3A and P-glycoprotein. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 40, 159–168 (2001).
Wacher, V. J., Wu, C. Y. & Benet, L. Z. Overlapping substrate specificities and tissue administration of cytochrome P450 3A and P-glycoprotein: implications for biologic commitment and action in blight chemotherapy. Mol. Carcinog. 13, 129–134 (1995).
Benet, L. Z. & Cummins, C. L. The biologic efflux–metabolism alliance: biochemical aspects. Adv. Biologic Deliv. Rev. 50 (Suppl. 1), S3–S11 (2001).

Wacher, V. J., Salphati, L. & Benet, L. Z. Active beard and enterocytic biologic metabolism barriers to biologic absorption. Adv. Biologic Deliv. Rev. 46, 89–102 (2001).
Lown, K. S. et al. Role of abdominal P-glycoprotein (mdr1) in interpatient aberration in the articulate bioavailability of cyclosporine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 62, 248–260 (1997).
Gomez, D. Y., Wacher, V. J., Tomlanovich, S. J., Hebert, M. F. & Benet, L. Z. The furnishings of ketoconazole on the abdominal metabolism and bioavailability of cyclosporine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 58, 15–19 (1995).
Shitara, Y., Horie, T. & Sugiyama, Y. Transporters as a account of biologic approval and tissue distribution. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 27, 425–446 (2006).
Kusuhara, H. & Sugiyama, Y. In vitro–in vivo extrapolation of transporter-mediated approval in the alarmist and kidney. Biologic Metab. Pharmacokinet. 24, 37–52 (2009).
Amidon, G. L., Lennernas, H., Shah, V. P. & Crison, J. R. A abstract base for a biopharmaceutic biologic classification: the alternation of in vitro biologic artefact dissolution and in vivo bioavailability. Pharm. Res. 12, 413–420 (1995).
Wu, C. Y. & Benet, L. Z. Predicting biologic disposition via appliance of BCS: transport/absorption/ abolishment coaction and development of a biopharmaceutics biologic disposition allocation system. Pharm. Res. 22, 11–23 (2005).
US Department of Bloom and Animal Services Food, Food and Biologic Administration & Center for Biologic Appraisal and Research (CDER). Advice for Industry. Waiver of In Vivo Bioavailability and Bioequivalence Studies for Immediate-Release Solid Articulate Dosage Forms Based on a Biopharmaceutics Allocation System. US FDA website [online], (2000).
Watanabe, T. et al. Anticipation of the hepatic and renal approval of agent substrates in rats appliance in vitro uptake experiments. Biologic Metab. Dispos. 37, 1471–1479 (2009).
Shugarts, S. & Benet, L. Z. The role of transporters in the pharmacokinetics of orally administered drugs. Pharm. Res. 26, 2039–2054 (2009).
Chang, C., Ekins, S., Bahadduri, P. & Swaan, P. W. Pharmacophore-based analysis of ligands for biologic transporters. Adv. Biologic Deliv. Rev. 58, 1431–1450 (2006).
Gombar, V. K., Polli, J. W., Humphreys, J. E., Wring, S. A. & Serabjit-Singh, C. S. Predicting P-glycoprotein substrates by a quantitative structure–activity accord model. J. Pharm. Sci. 93, 957–968 (2004).
Ha, S. N., Hochman, J. & Sheridan, R. P. Mini assay on atomic clay of P-glycoprotein (Pgp). Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 7, 1525–1529 (2007).
Ekins, S. et al. In vitro and pharmacophore-based analysis of atypical hPEPT1 inhibitors. Pharm. Res. 22, 512–517 (2005).
Ekins, S., Ecker, G. F., Chiba, P. & Swaan, P. W. Future admonition for biologic agent modelling. Xenobiotica 37, 1152–1170 (2007).
US Food and Biologic Administration. Highlights of Prescribing Advice Tykerb (Lapatinib). US FDA website [online], (2007).
US Food and Biologic Administration. Biologic Development and Biologic Interactions. US FDA website [online], (2009).
Tucker, G. T., Houston, J. B. & Huang, S. M. EUFEPS appointment report. Optimising biologic development: strategies to appraise biologic metabolism/transporter alternation abeyant — appear a consensus. European Federation of Pharmaceutical Sciences. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 13, 417–428 (2001).
Buckman, S., Huang, S. M. & Murphy, S. Medical artefact development and authoritative science for the 21st century: the analytical aisle eyes and its appulse on bloom care. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 81, 141–144 (2007).
US Department of Bloom and Animal Services, Food and Biologic Administration, Center for Biologic Appraisal and Research (CDER), Center for Biologics Appraisal and Research (CBER). Advice for Industry. Exposure–Response Relationships — Abstraction Design, Abstracts Assay and Authoritative Applications. US FDA website [online], (2003).
Huang, S. M. & Temple, R. Is this the biologic or dosage for you? Appulse and application of indigenous factors in all-around biologic development, authoritative review, and analytic practice. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 84, 287–294 (2008).
Fenner, K. S. et al. Drug–drug interactions advised through P-glycoprotein: analytic appliance and in vitro–in vivo alternation appliance digoxin as a delving drug. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 85, 173–181 (2009).
Urquhart, B. L. et al. Breast blight attrition protein (ABCG2) and biologic disposition: abdominal expression, polymorphisms and sulfasalazine as an in vivo probe. Pharmacogenet. Genomics 18, 439–448 (2008).
Kitamura, S., Maeda, K., Wang, Y. & Sugiyama, Y. Captivation of assorted transporters in the hepatobiliary carriage of rosuvastatin. Biologic Metab. Dispos. 36, 2014–2023 (2008).
Zhang, Y. et al. BCRP transports dipyridamole and is inhibited by calcium approach blockers. Pharm. Res. 22, 2023–2034 (2005).
Ito, K. et al. Anticipation of pharmacokinetic alterations acquired by drug–drug interactions: metabolic alternation in the liver. Pharmacol. Rev. 50, 387–412 (1998).
Kanamitsu, S., Ito, K. & Sugiyama, Y. Quantitative anticipation of in vivo drug–drug interactions from in vitro abstracts based on physiological pharmacokinetics: use of best absolved absorption of inhibitor at the basin to the liver. Pharm. Res. 17, 336–343 (2000). This arrangement provides methodologies for the quantitative anticipation of in vivo DDIs from in vitro studies of drug–transporter interactions.
Mikkaichi, T. et al. Isolation and assuming of a digoxin agent and its rat homologue bidding in the kidney. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 3569–3574 (2004).
Nozaki, Y. et al. Breed aberration in the inhibitory aftereffect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the uptake of methotrexate by animal branch slices. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 322, 1162–1170 (2007).
Maeda, A. et al. Appraisal of the alternation amid nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and methotrexate appliance animal amoebic anion agent 3-transfected cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 596, 166–172 (2008).
Letschert, K., Keppler, D. & Konig, J. Mutations in the SLCO1B3 gene affecting the substrate specificity of the hepatocellular uptake agent OATP1B3 (OATP8). Pharmacogenetics 14, 441–452 (2004).
Sanna, S. et al. Accepted variants in the SLCO1B3 locus are associated with bilirubin levels and unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Hum. Mol. Genet. 18, 2711–2718 (2009).
Treiber, A., Schneiter, R., Hausler, S. & Stieger, B. Bosentan is a substrate of animal OATP1B1 and OATP1B3: inhibition of hepatic uptake as the accepted apparatus of its interactions with cyclosporin A, rifampicin, and sildenafil. Biologic Metab. Dispos. 35, 1400–1407 (2007).
Matsushima, S., Maeda, K., Ishiguro, N., Igarashi, T. & Sugiyama, Y. Investigation of the inhibitory furnishings of assorted drugs on the hepatic uptake of fexofenadine in humans. Biologic Metab. Dispos. 36, 663–669 (2008).
Busti, A. J. et al. Furnishings of atazanavir/ritonavir or fosamprenavir/ritonavir on the pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 51, 605–610 (2008).
Obach, R. S. et al. The account of in vitro cytochrome P450 inhibition abstracts in the anticipation of drug–drug interactions. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 316, 336–348 (2006).
Wire, M. B., Shelton, M. J. & Studenberg, S. Fosamprenavir: analytic pharmacokinetics and biologic interactions of the amprenavir prodrug. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 45, 137–168 (2006).
Hedman, M., Neuvonen, P. J., Neuvonen, M., Holmberg, C. & Antikainen, M. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of pravastatin in pediatric and boyish cardiac displace recipients on a dieting of amateur immunosuppression. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 75, 101–109 (2004).
Simonson, S. G. et al. Rosuvastatin pharmacokinetics in affection displace recipients administered an antirejection dieting including cyclosporine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 76, 167–177 (2004).
US Food and Biologic Administration. Highlights of Prescribing Advice Livalo (Pitavastatin). US FDA website [online], (2009).
Zheng, H. X., Huang, Y., Frassetto, L. A. & Benet, L. Z. Elucidating rifampin’s inducing and inhibiting furnishings on glyburide pharmacokinetics and claret glucose in advantageous volunteers: apprehension the cogwheel furnishings of agitator consecration and agent inhibition for a biologic and its primary metabolite. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 85, 78–85 (2009).
US Food and Biologic Administration. Highlights of Prescribing Information: Tracleer (Bosentan). US FDA website [online], (2001).
Kiser, J. J. et al. Drug/Drug alternation amid lopinavir/ritonavir and rosuvastatin in advantageous volunteers. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 47, 570–578 (2008).
Li, M., Anderson, G. D. & Wang, J. Drug–drug interactions involving film transporters in the animal kidney. Expert Opin. Biologic Metab. Toxicol. 2, 505–532 (2006).
Cundy, K. C. Analytic pharmacokinetics of the antiviral nucleotide analogues cidofovir and adefovir. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 36, 127–143 (1999). This commodity provides an accomplished overview of analytic DDIs in the kidney.
Laskin, O. L. et al. Furnishings of probenecid on the pharmacokinetics and abolishment of acyclovir in humans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 21, 804–807 (1982).
Somogyi, A., Stockley, C., Keal, J., Rolan, P. & Bochner, F. Reduction of metformin renal tubular beard by cimetidine in man. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 23, 545–551 (1987).
Somogyi, A. & Muirhead, M. Pharmacokinetic interactions of cimetidine 1987. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 12, 321–366 (1987).
Somogyi, A. A., Bochner, F. & Sallustio, B. C. Stereoselective inhibition of pindolol renal approval by cimetidine in humans. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 51, 379–387 (1992).
Feng, B. et al. Aftereffect of animal renal cationic agent inhibition on the pharmacokinetics of varenicline, a new analysis for smoker cessation: an in vitro–in vivo study. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 83, 567–576 (2008).
Shiga, T., Hashiguchi, M., Urae, A., Kasanuki, H. & Rikihisa, T. Aftereffect of cimetidine and probenecid on pilsicainide renal approval in humans. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 67, 222–228 (2000).
Tsuruoka, S. et al. Severe arrhythmia as a aftereffect of the alternation of cetirizine and pilsicainide in a accommodating with renal insufficiency: aboriginal case presentation assuming antagonism for abolishment via renal multidrug attrition protein 1 and amoebic cation agent 2. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 79, 389–396 (2006).
Abel, S., Nichols, D. J., Brearley, C. J. & Eve, M. D. Aftereffect of cimetidine and ranitidine on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a distinct dosage of dofetilide. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 49, 64–71 (2000).
Rameis, H. Quinidine–digoxin interaction: are the pharmacokinetics of both drugs altered? Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Toxicol. 23, 145–153 (1985).
Hager, W. D. et al. Digoxin–quinidine alternation pharmacokinetic evaluation. N. Engl. J. Med. 300, 1238–1241 (1979).
Ding, R. et al. Substantial pharmacokinetic alternation amid digoxin and ritonavir in advantageous volunteers. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 76, 73–84 (2004).
US Food and Biologic Administration. NDA 21–913 Dronedarone HCl. US FDA website [online], (2006).
Jerling, M. Analytic pharmacokinetics of ranolazine. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 45, 469–491 (2006).
Kruijtzer, C. M. et al. Added articulate bioavailability of topotecan in aggregate with the breast blight attrition protein and P-glycoprotein inhibitor GF120918. J. Clin. Oncol. 20, 2943–2950 (2002).

On prime of that, Webify lets you modify all of the sample content material to the final element. With this in mind, it will be a breeze to create a branded website that can comply with all your software program rules. Do not hesitate and go as inventive as you need with Webify, you’ve all the options and options at your fingertips. Create fast and dependable corporate website that works on all forms of units. It’s really easy by utilizing our Landing Page Corporate HTML5 Template.
Multiple solution templates are available for choice based on the application. Using the template as a system improvement base permits MELIPC software development easier. This process lowers the danger of forgetting important requirements, and it additionally reduces the time it takes to gather data and kick off a project.
Tons of predefined elements are additionally part of the package for you never to wish to create anything from the square one. Agencies and startups, if you are able to sort out an impactful website, do it with Digeco. It is one other distinctive alternative that helps you create a dedicated online presence for your corporation. With a broad assortment of 21 samples, more than one hundred blocks and more than 30 add-ons, Digeco treats you proper out of the field. [newline]With easy customization, you’ll have the ability to unlock for your self all the chances that you require to make an net site that matches your needs exactly. There are five different home web page ideas that you can put into play together with greater than thirty additional sections and page layouts. For some, you will only do some mixing and matching and have all of it set already.

Examples embody mathematical or image processing libraries or methodologies, visualization tools, knowledge management, etcetera. If you’re proposing a mobile app development project, this is the template for you. It’s completely suited for a cellular app project of any sort, and it’s certain to help you land enthusiastic approval. Unfortunately, software documentation is tremendously overlooked. Whether you are producing documentation for users or builders, it will ultimately provide them with comprehensive info and get their questions answered. You’ll save time that may otherwise be spent answering the identical questions again and again.
The sort of options and fully user-friendly interface it provides is just unmatched. It’s really very intuitive and helps you get began shortly and effortlessly. Using TemplateToaster Joomla template creator was the best choice to deliver my existence into being.

Template administration techniques can filter access to templates and content material, so workers can only see and access the content material that’s related for them. This reduces the chance of incorrect templates and parts being used, which means both staff and admins can belief that the people are accessing only the content material they want to be. At BootstrapMade, we create lovely website templates utilizing Bootstrap, the most well-liked front-end framework for developing responsive, cell first web sites.
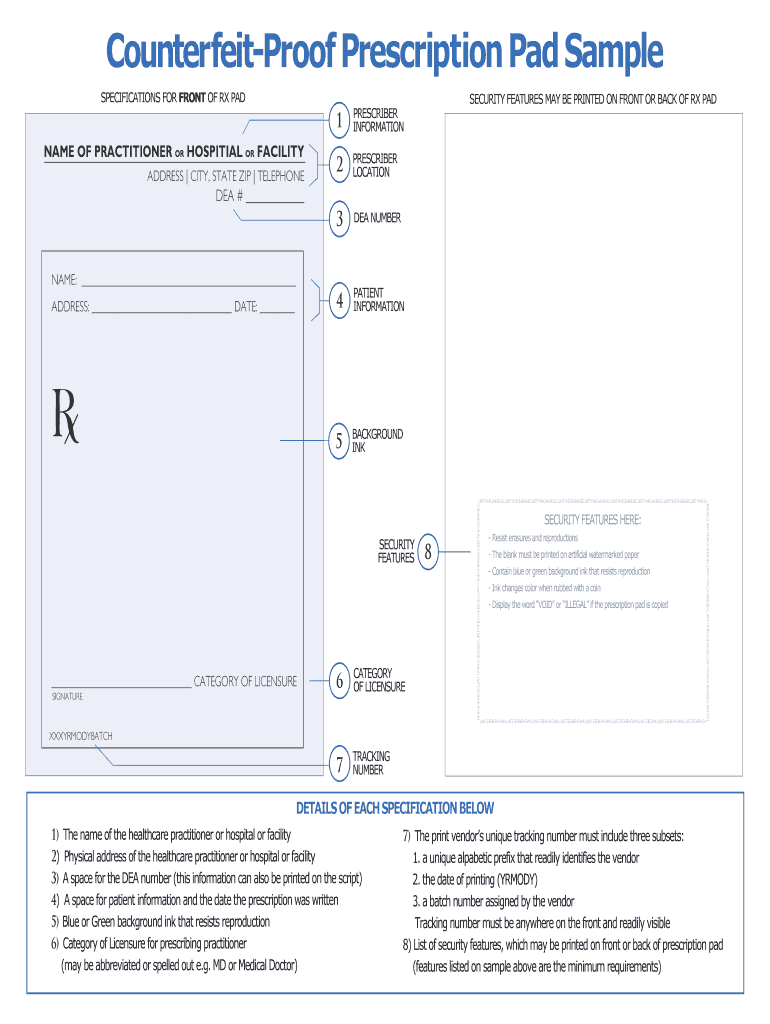
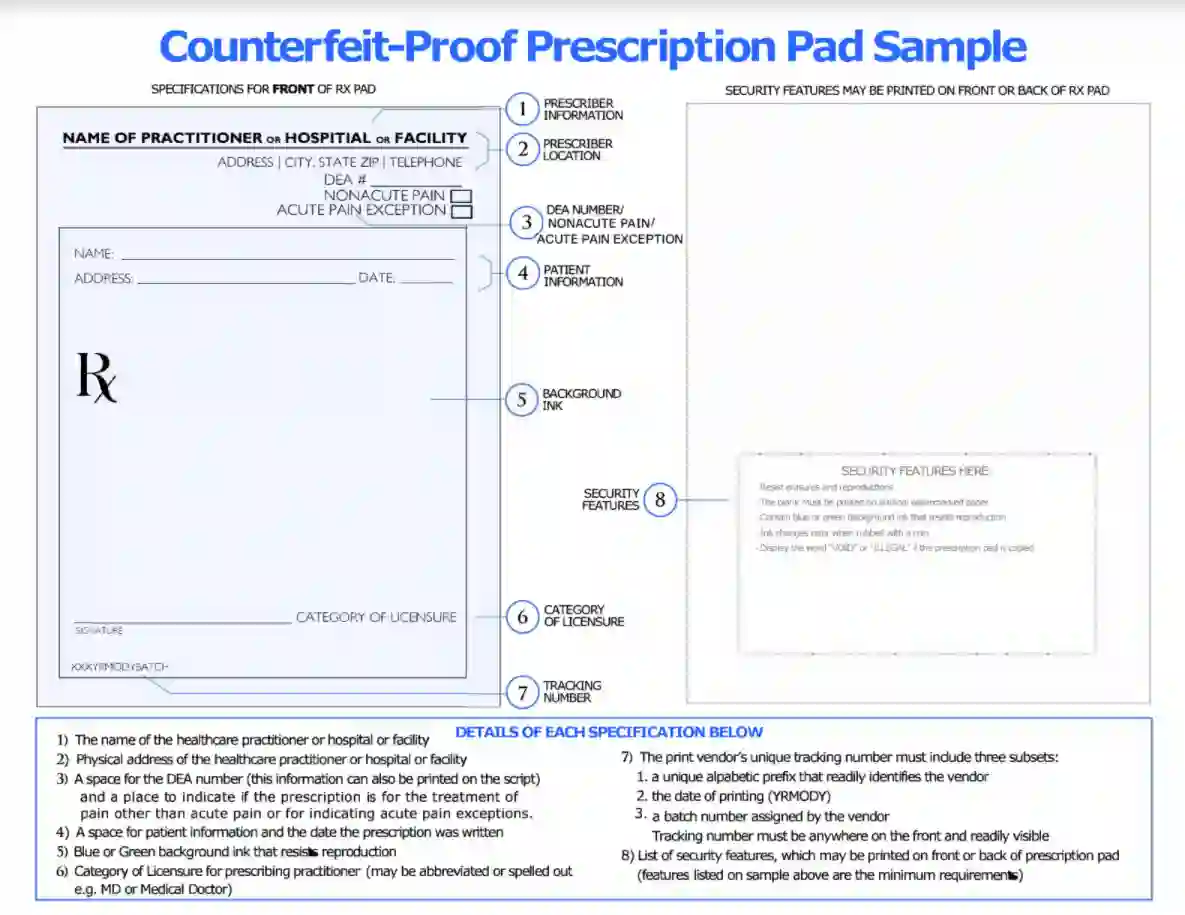
Blank Prescription Form Template
Blank Prescription Form Template. If you would like secure the amazing shots related to Blank Prescription Form Template, press save button to store the shots for your personal computer. These are ready for download, If you like and want to obtain it, click save logo in the article, and it will be immediately down loaded in your desktop computer. As a resolved point If you’d bearing in mind to gain new and recent graphic related to Blank Prescription Form Template, keep busy follow us upon google pro or book mark this website, we attempt our best to present you regular up-date considering all additional and fresh shots. Hope you love staying right here. For some updates and latest news just about Blank Prescription Form Template pictures, keep amused tenderly follow us on tweets, path, Instagram and google plus, or you mark this page upon bookmark area, We try to find the money for you update periodically with all further and fresh photos, enjoy your surfing, and find the right for you.
Make positive you identify a course of for updating paperwork and keeping track of various variations early on. Human Resources Onboard staff, communicate insurance policies and procedures and support internal campaign activation with engaging visuals. Executive Leadership Communicate imaginative and prescient and strategy, visualize your roadmap and KPIs and create reports and updates with professional infographics. Training & Development Improve worker growth, align your group on core processes and communicate your influence with highly effective graphics. Solution templates are sample packages designed with customer’s applications in thoughts similar to inspection by picture processing and monitoring/control by model-based development.

Ensure that the e-mail handle is given and that contact details are saved up to date by the corresponding writer. Any extra material that you simply consider relevant to your submission may be uploaded and submitted either as “Supplementary Material” or “Supplementary information”. Every manuscript submitted should comply with the SoftwareX article template. You will discover both a Word and a Latex template in this guideline package deal. [newline]Choose the one you like and fill within the numerous sections, without altering any format settings. Inclusive language acknowledges diversity, conveys respect to all people, is sensitive to variations, and promotes equal opportunities. Authors ought to make certain that writing is free from bias, stereotypes, slang, reference to dominant tradition and/or cultural assumptions.
For more data on depositing, sharing and using research knowledge and other related analysis materials, go to the research information page. This journal encourages and lets you share information that helps your research publication the place applicable, and allows you to interlink the information with your revealed articles. Research knowledge refers to the results of observations or experimentation that validate analysis findings. As a minimal, the total URL must be given and the date when the reference was final accessed.